A Clinician’s Handbook for Childhood & Adult Immunizations in Georgia
How to Administer Intramuscular and Subcutaneous Vaccine Injections
Administration by the Intramuscular (IM) Route
Administer these vaccines via IM route
- Diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis (DTaP, Tdap)
- Diphtheria-tetanus (DT, Td)
- Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib)
- Hepatitis A (HepA)
- Hepatitis B (HepB)
- Human papillomavirus (HPV)
- Inactivated influenza (IIV)
- Meningococcal serogroups A,C,W, Y (MenACWY)
- Meningococcal serogroup B (MenB)
- Pneumococcal conjugate (PCV)
- Zoster, recombinant (RZV)
Administer inactivated polio (IPV) and pneumococcal polysaccharide (PPSV23) vaccines either IM or subcutaneously (Subcut).
CDC. “General Best Practices Guidelines for
Immunization: Best Practices Guidance of
the ACIP” at How to Administer Intramuscular and Subcutaneous Vaccine Injections to Adults (immunize.org)
| patient age | injection site | needle size |
|---|---|---|
| Newborn (0–28 days) | Anterolateral thigh muscle | ⅝"* (22–25 gauge) |
| Infant (1–12 mos) | Anterolateral thigh muscle | 1" (22–25 gauge) |
| Toddler (1–2 years) | Anterolateral thigh muscle | 1–1¼" (22–25 gauge) |
| Toddler (1–2 years) | Alternate site: Deltoid muscle of arm if muscle mass is adequate | ⅝*–1" (22–25 gauge) |
| Children (3–10 years) | Deltoid muscle (upper arm) | ⅝*–1" (22–25 gauge) |
| Children (3–10 years) | Alternate site: Anterolateral thigh muscle | 1–1¼" (22–25 gauge) |
| Children and adults (11 years and older) | Deltoid muscle (upper arm) | ⅝†–1" (22–25 gauge) |
| Children and adults (11 years and older) | Alternate site: Anterolateral thigh muscle | 1–1½" (22–25 gauge) |
* A ⅝” needle usually is adequate for neonates (first 28 days of life), preterm infants, and children ages 1 through 18 years if the skin is stretched flat between the thumb and forefinger and the needle is inserted at a 90° angle to the skin.
† A ⅝” needle may be used in patients weighing less than 130 lbs (<60 kg) for IM injection in the deltoid muscle only if the skin is stretched flat between the thumb and forefinger and the needle is inserted at a 90º angle to the skin; a 1″ needle is sufficient in patients weighing 130–152 lbs (60–70 kg); a 1–1½” needle is recommended in women weighing 153–200 lbs (70–90 kg) and men weighing 153–260 lbs (70–118 kg); a 1½” needle is recommended in women weighing more than 200 lbs (91 kg) or men weighing more than 260 lbs (118 kg).
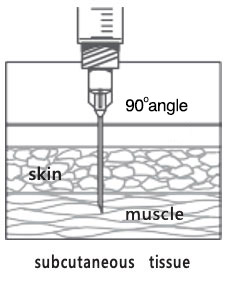
Needle Insertion
Use a needle long enough to reach deep into the muscle.
Insert needle at a 90° angle to the skin with a quick thrust. (Before administering an injection of vaccine, it is not necessary to aspirate, i.e., to pull back on the syringe plunger after needle insertion.)
Multiple injections given in the same extremity should be separated by a minimum of 1″, if possible.
Intramuscular (IM) Injection Site for Infants and Toddlers
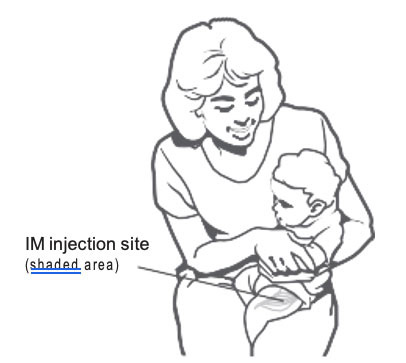
Insert needle at a 90° angle into the anterolateral thigh muscle.
Intramuscular (IM) Injection Site for Children and Adults
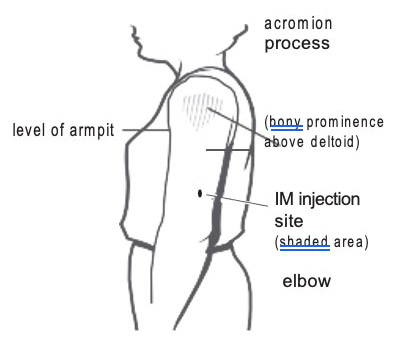
Give in the central and thickest portion of the deltoid muscle – above the level of the armpit and approximately 2–3 fingerbreadths (~2″) below the acromion process. See the diagram. To avoid causing an injury, do not inject too high (near the acromion process) or too low.
Administration by the Subcutaneous (Subcut) Route
Administer these vaccines via Subcut routeMeasles, mumps, and rubella (MMR)
- Measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR)
- Varicella (VAR)
- Zoster, live (ZVL)
Administer inactivated polio (IPV) and pneumococcal polysaccharide (PPSV23) vaccines either IM or Subcut.
CDC. “General Best Practices Guidelines for
Immunization: Best Practices Guidance of
the ACIP” at How to Administer Intramuscular and Subcutaneous Vaccine Injections to Adults (immunize.org)
| patient age | injection site | needle size |
|---|---|---|
| Birth to 12 months | Fatty tissue overlying the anterolateral thigh muscle | ⅝" (23–25 gauge) |
| 12 months and older | Fatty tissue overlying the anterolateral thigh muscle or fatty tissue over triceps | ⅝" (23–25 gauge) |
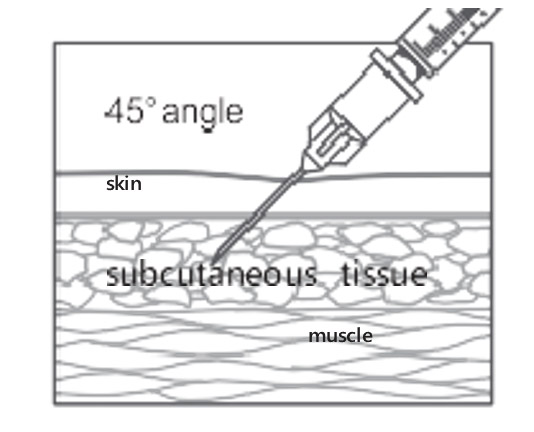
Needle insertion
Pinch up on subcutaneous tissue to prevent injection into muscle.
Insert needle at 45° angle to the skin. (Before administering an injection of vaccine, it is not necessary to aspirate, i.e., to pull back on the syringe plunger after needle insertion.*)
Multiple injections given in the same extremity should be separated by a minimum of 1″.
Subcutaneous (Subcut) injection site for infants
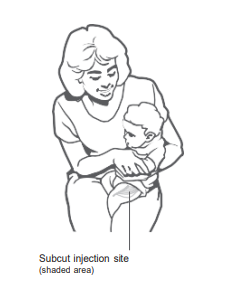
Insert needle at a 45° angle into fatty tissue of the anterolateral thigh. Make sure you pinch up on subcutaneous tissue to prevent injection into the muscle.
Subcutaneous (Subcut) injection site for children (after the 1st birthday) and Adults
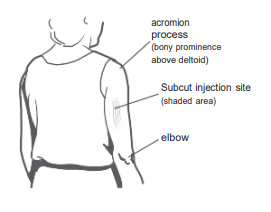
Insert needle at a 45° angle into the fatty tissue overlying the triceps muscle. Make sure you pinch up on the subcutaneous tissue to prevent injection into the muscle.
